SLS and DMLS are both powder bed fusion technologies that create parts from a powder. SLS uses a laser to sinter a plastic powder into a part. DMLS, on the other hand, uses a high-powered laser to sinter metal powder into a high-performance part. SLS is cheaper, whereas DMLS-produced items have significantly better mechanical properties due to the parts being metal. As such, DMLS is ideal for functional parts used in extreme environments, whereas SLS can be used for low-performance functional parts or visual prototypes. Printing speeds are comparable between SLS and DMLS, however, DMLS is significantly more expensive per part.
This article will compare SLS vs. DMLS in terms of their differences, materials, and printing technology.
SLS Definition and Comparison to DMLS
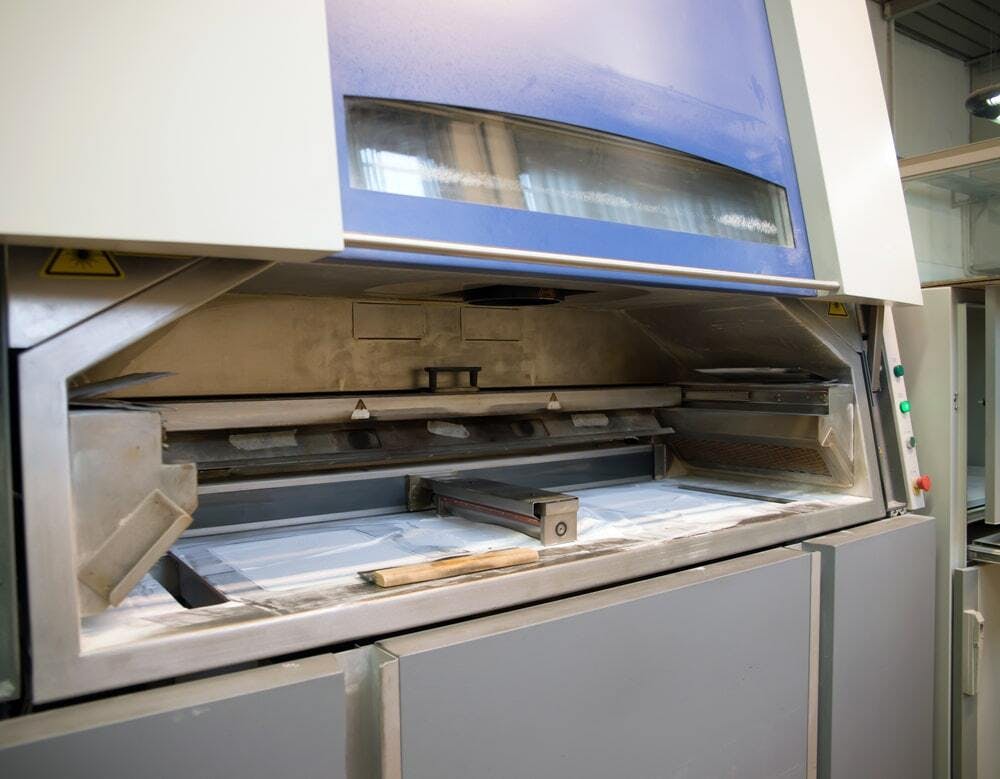
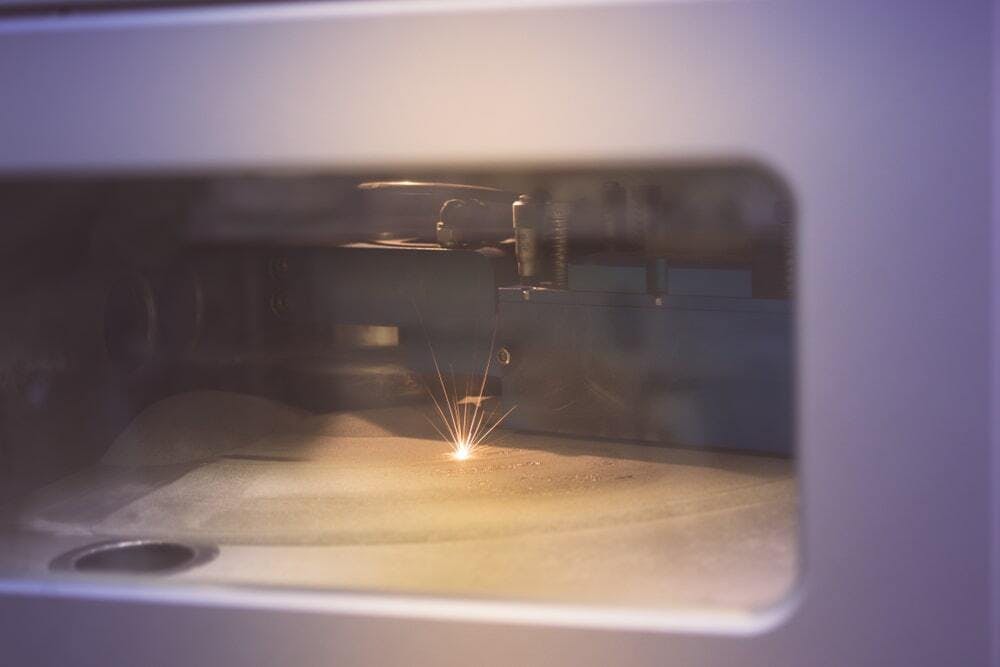
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) is a plastic powder bed 3D printing technology that makes use of a sintering process. It was first invented by Dr. Carl Deckard and Dr. Joe Beaman in the mid-1980s. SLS works by selectively sintering a plastic powder with a laser beam (typically a CO2 laser). The laser beam traces out the cross-section of a part layer and sinters the plastic particles together. After each layer, the print bed moves down and another layer of powder is applied. Sintering refers to the process of heating the plastic particles to the point where their outside surfaces begin melting. This causes the individual particles to stick together. SLS primarily works with plastic whereas DMLS works with metal. Below is an image of a typical SLS machine:
A typical SLS machine.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/Moreno Soppelsa
What Are the Advantages of SLS Compared to DMLS?
Listed below are some key advantages of SLS vs.DMLS:
- SLS can produce cheaper prototypes like those used to check product form (i.e., visual properties) and product fit (i.e., interfacing with other components) compared to DMLS.
- SLS parts do not need support when printing.
- SLS parts can be dyed in multiple colors.
What Are the Disadvantages of SLS Compared to DMLS?
Listed below are some key disadvantages of SLS vs. DMLS:
- SLS can only print plastic parts.
- Parts printed with SLS are significantly weaker than those printed with DMLS due to SLS parts being plastic.
DMLS Definition and Comparison to SLS
DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering) is a powder bed fusion 3D printing technology that is used to manufacture metal parts. EOS first commercialized the technology in 1995. This process works by selectively sintering a metal or metal alloy powder with a high-powered laser beam (typically a CO2 laser or a fiber laser). The laser beam traces out the cross-section of a part layer and sinters the metal particles together. After each layer, the print bed moves down and another layer of metal powder is applied. The metal powder is preheated to close to its sintering temperature. DMLS also fills the build chamber with an inert gas to prevent oxidation during printing. Below is an image of how DMLS works:
How a DMLS machine works.
Image Credit: Shutterstock.com/MarinaGrigorivna
What Are the Advantages of DMLS Compared to SLS?
Listed below are some key advantages of DMLS vs. SLS:
- DMLS is capable of printing high-strength functional metal parts in a wide variety of metals.
- It is possible to print material mixtures of nylon and aluminum.
What Are the Disadvantages of DMLS compared to SLS?
Listed below are some key disadvantages of DMLS vs. SLS:
- Due to the materials used, DMLS is significantly more expensive than SLS. It has higher energy requirements, a gas-filled build chamber, and a more expensive raw material.
- DMLS parts need support during printing. This is due to the increased mass of metal parts.
Comparison Table Between SLS and DMLS
The table below lists some of the more common properties of SLS vs. DMLS as well as how they compare with each other:
Print resolution
100 microns
154 microns
Can print large parts
Yes
Yes
Can print in metal
No
Yes
Can print in plastic & metal
No
Yes
Can be dyed in multiple colors
Yes
No
Minimum feature size
0.75 mm
0.635 mm
Has isotropic material properties
Yes
Yes
Can recycle more than 80% of unused powder
No
Yes
Parts need to be cooled after printing
Yes
Yes
Parts need support structures
No
Yes
Largest print volume
550 x 550 x 750 mm
400 x 400 x 400 mm
Table. SLS vs. DMLS Comparison
DMLS and SLS have similar resolution and minimum feature size. However, DMLS can print in metal and the powder is more recyclable. SLS parts do not need any support structures, unlike DMLS parts.
SLS vs. DMLS: Technology Comparison
Fundamentally SLS and DMLS share the same technology, i.e., powder bed fusion. The difference lies in the power of the laser and the fact that DMLS machines need to have their build volumes filled with an inert gas during printing.
SLS vs. DMLS: Material Comparison
SLS can print in a variety of polyamides including: Nylon 12 and elastomeric materials like TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane). DMLS is primarily a metal printing technology that can print in stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, nickel alloys, and some precious metals. DMLS is also able to print in nylon.
SLS vs. DMLS: Product Applications Comparison
SLS is primarily used for products that don’t need to be used in high-load and high-temperature environments. SLS parts are also used for functional and visual prototypes. DMLS, however, is better suited to printing high-performance products and components that are exposed to extreme environments like those found in the aerospace and automotive industries.
SLS vs. DMLS: Print Volume Comparison
SLS and DMLS have comparable build volumes, with SLS machines having slightly larger volumes than more high-end machines. DMLS parts become significantly more expensive as their size increases.
SLS vs. DMLS: Surface Finish Comparison
Due to the nature of the sintering process, both technologies will produce parts that have a rough/matte surface finish. Both technologies can have their parts post-processed to improve surface quality. Typical processes can include: tumbling, bead blasting, and polishing; whereas only polishing is possible on DMLS metal parts.
SLS vs. DMLS: Cost Comparison
SLS is significantly cheaper than DMLS. This is due to the high cost of the metal powder, high energy consumption, as well as the more expensive machines used for DMLS printing.
What are the Mutual Alternatives to SLS and DMLS?
Despite the benefits of SLS and DMLS, there are alternative technologies that can achieve similar results:
- Desktop Metal: This process prints parts by using a process similar to FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) to print a part with a metal powder bound in a polymer matrix. The parts are then transferred to a furnace where they are sintered into a final metal part.
What Are the Similarities Between SLS and DMLS?
Listed below are some of the similarities between SLS vs. DMLS:
- Both technologies make use of powder bed fusion to manufacture parts.
- SLS and DMLS can print nylon parts.
- Complex, high-quality parts can be manufactured with both technologies.
- SLS and DMLS produce parts that have isotropic properties.
What Are the Other Comparisons for SLS Besides DMLS?
Other comparison technologies for SLS include:
- SLS vs. MJF: Multi Jet Fusion is a suitable alternative to SLS. It can print with similar resolution and materials. MJF also has improved mechanical properties. For more information, see our article on SLS vs. MJF.
- SLS vs. Binder Jetting: Binder jetting is functionally similar to MJF. But, instead of a laser fusing the powder, a binding agent is applied with an inkjet-type printing head to fuse the particles. Post-curing is required to create strong parts.
What Are the Other Comparisons for DMLS Besides SLS?
Other comparison technologies for DMLS include:
- DMLS vs. EBM: Electron Beam Melting is also a powder bed fusion technology. But, instead of using a laser, an electron beam is used to melt the metal powder into a final part. This produces parts that have homogenous mechanical properties.
- DMLS vs. DED: Directed-energy Deposition is a metal printing technology that feeds a metal wire to a printing nozzle. The metal is then melted at the nozzle and deposited on the build plate layer by layer, similar to FDM printing. This produces parts that have homogenous mechanical properties.
Summary
This article summarized the differences between SLS and DMLS 3D printing technologies.
To learn more about SLS vs. DMLS and to help select the perfect technology for your products, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry offers a full range of 3D printing services for your project needs. Visit our Instant Quote Engine to get a free, no-obligation quote in minutes.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.

.webp)